Choreography
Animation sequence requires understanding of what will be entering the screen, what has left the screen and
what remains. For each of these states, it is important to define the proper timing and apply the easing
methods. Once you apply this framework, you can successfully choreograph the sequence of interactions on a
given screen.
Screen transitions
incoming:
ease-out


persistent:
ease-in-out


outgoing:
ease-in


0ms
300ms
450ms
1650ms
Outgoing
screen exits the screen
screen enters the screen
screen starts and end on screen
Incoming
Persistent
Screens in a sequence are categorized as outgoing, incoming, or persistent.
Elements transitions
outgoing:
ease-in


outgoing:
ease-in


incoming:
ease-out

incoming:
ease-out

persistent:
ease-in-out

0ms
50ms
200ms
300ms
350ms
1550ms
1650ms
Outgoing
elements exit the screen
elements enter the screen
elements start and end on screen
Incoming
Persistent
UI elements in a sequence are categorized as outgoing, incoming, or persistent. Every element has its own
transition speed depending on its size and meaning. Outgoing elements are exiting the screen one
after another with 50ms interval and at the same time incoming elements are entering the screen with 150ms
accordingly.


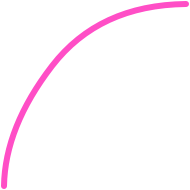
iOS
Design system usage:
ease-out

After Effects
Outgoing velocity:
0,01
Incoming velocity:
100%
Ease-out: element entering the screen
After Effects
Outgoing velocity:
100%
Incoming velocity:
0.01%


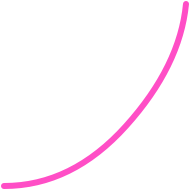
iOS
Design system usage:
ease-in

Ease-in: element exiting the screen
After Effects
Outgoing velocity:
42%
Incoming velocity:
42%


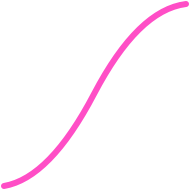
iOS
Design system usage:
ease-in-out

Ease-in-out: element presistin on the screen
Easing
Download assets

Motion helps orient users by showing how elements are related to one another, explain changes in states, draw
attention to necessary actions, determine relationships between elements. Using deliberate motion can both
acknowledge user input, and help them navigate through information without losing their bearings.
Motion design is a powerful tool in designing and building communication and user experience. It can bring
your work to life, guide users through complex experiences.